Skin Cancer

Skin is the largest organ in the body. It is also the fastest growing and has its own metabolism. It is made up of 19 million cells per square inch, sheds 30,000 cells per minute and accounts for 10 to 15% of your body weight.
Our skin is made of two layers, the dermis and the epidermis. The epidermis is less than 1mm thick and is the outermost layer, carrying out most of the barrier functions to protect us from physical damage as well as being waterproof. The dermis is the inner layer and contains the connective tissue, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands and hair follicles.
The skin is an extraordinary organ, but like all organs it can develop cancer.
There are two types of skin cancer: melanoma and non-melanoma, which is the more common of the two.
Non-melanoma skin cancer is a type of cancer that starts on the top layer of skin (the epidermis). The main types are basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma. The main cause is UV (ultra-violet) light, which comes from the sun and from sunbeds.
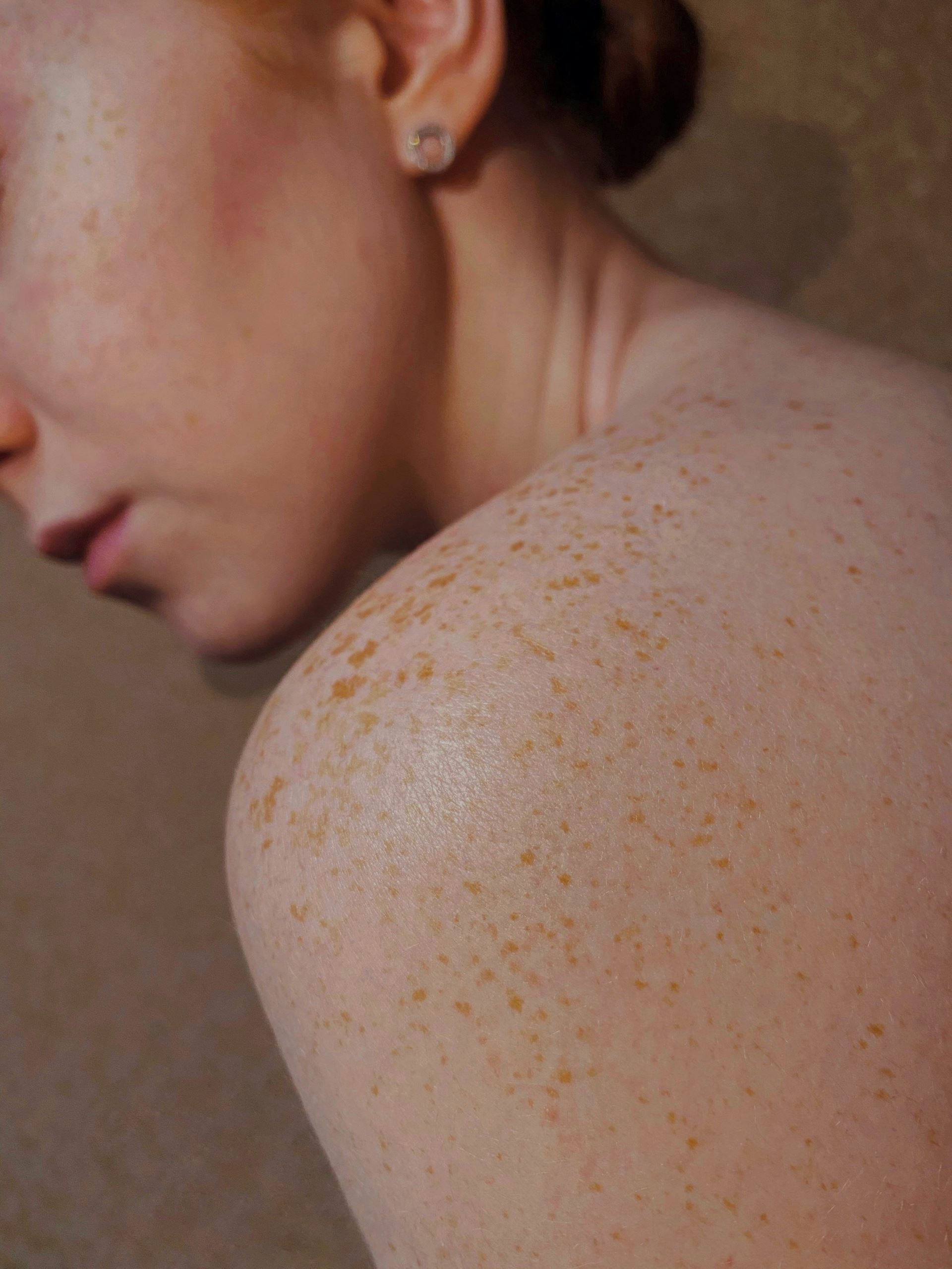
The main symptom of non-melanoma skin cancer is an unusual growth or patch of skin. Any part of your body can be affected, but it is most common in areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, head, legs, arms, neck and hands.
The growths can vary in size and shape, so if you notice something different on your skin that gets bigger, changes colour or texture, or hurts, itches, bleeds or scabs, make an appointment with your doctor. Non-melanoma skin cancer is easily treated, but the soonder it is found, the easier it is to treat.
Treatment generally involves excising (cutting out) the growth or cryosurgery (freezing the affected skin). Radiotherapy may also be used if the cancer covers a large area, is in a difficult location or if you are too unwell for surgery.
Melanoma skin cancer is a type of skin cancer that starts in the cells that produce melanin, the cells that give skin its colour. It can can spread to other areas of the body. Like non-melanoma cancer, it is mainly caused by UV light and is most common in areas that are exposed to the sun.
The main symptom of melanoma skin cancer is a new mole or a change to an existing mole and could be itchy, painful, bleeding or crusty. If you notice a new mole, or an existing mole has changed size, shape or colour, make an appointment with your doctor immediately.
Melanoma can often be treated. Surgery is the main treatment, especially if the cancer is caught early. As well as removing the melanoma, healthy skin around it may be removed to lower the chances of it returning. You may also have lymph glands or other areas of the body removed if the melanoma has spread to them. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy may also be used.
Support and Resources
Page created: 26 February 2021